How to differentiate between COLD and FLU?
Cold vs. flu facts
The common cold and flu share many symptoms, and it can be difficult or sometimes impossible to tell the difference based on symptoms alone. Medical tests can identify the flu.
A cold and the flu are both caused by viruses, but these viruses are different. Flu viruses are far more capable of causing more harm to the patient than cold viruses.
The flu and the common cold are both respiratory illnesses; flu can be far more serious and may cause significant problems in the respiratory system.
Symptoms of the common cold versus the flu may be distinguishable in a number of patients.
What is the common cold?
The common cold is a viral infection of the upper respiratory system (nose, throat, sinuses, Eustachian tubes, trachea, larynx, and bronchial tubes). About 30%-50% of colds are caused by rhinoviruses; however, more than 200 different viruses may cause the common cold. Colds are contagious and can be transmitted from person to person. Colds have an incubation period of about one to seven days (time from infection to appearance of symptoms). A cold's duration (how long it lasts) is about seven to 10 days; however, depending upon the viral strain, it can last up to two weeks. Colds are considered mainly to be a mild respiratory illness.
What is influenza?
Influenza (commonly termed the flu) is a viral infection of the upper respiratory and/or lower respiratory system caused by influenza viruses. These viruses usually cause more serious symptoms in the respiratory system than cold-causing viruses. The flu is contagious, can be transmitted from person to person, and has an incubation period of about one to four days. The flu's duration varies from about five days to two weeks depending upon the severity of the infection. The flu can become an intense and potentially fatal illness in some individuals.
What are causes and risk factors of a cold and the flu?
The causes of the flu are mainly influenza viruses belonging to either influenza A or influenza B types of viruses. The causes of colds are usually rhinoviruses, but over 200 types of viruses are capable of causing the common cold. Risk factors for the common cold and flu are similar or identical. Risk factors include the following:
Contact with a person who has either a cold or the flu -- especially contact with mucus membranes, saliva, and/or items that an infected person has touched (for example, towels, toothbrushes, and cups)
Contact with other objects that may be touched by an infected person such as handrails, doorknobs, and other high-use items
Risk is increased in individuals with compromised immune systems.
In general, the young and the old are usually more susceptible to these viruses.
Stress, smoking, and lack of sleep can increase your risk for getting these viral infections.
Individuals who do not receive the yearly flu vaccine are more likely to risk getting infected with a flu virus; unfortunately, because of the huge number of viruses that may cause a cold, there is no vaccine available commercially against the cold viruses.
How can someone tell the difference between the cold and the flu?
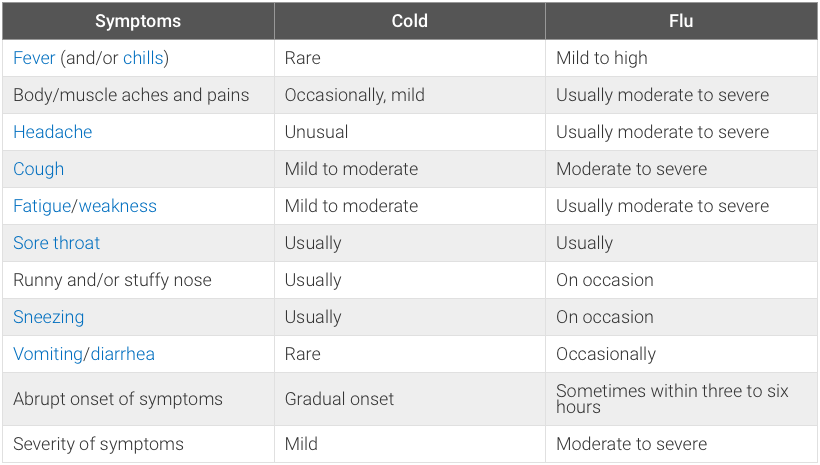
As stated previously, sometimes it's difficult, especially in the early stages of infection, to tell the difference between a cold and the flu. However, there are some symptoms, if present, that may help distinguish between colds and the flu. They are summarized in the chart below.
Differences between Cold and Flu
The above table shows the difficulty in diagnosing colds vs. flu using only symptoms; the best way is to do a short test for flu viruses done by trained medical caregivers.
What are the signs and symptoms of a cold and the flu?
The signs and symptoms of a cold or the flu are outlined in the table above. The flu symptoms are usually more intense than those seen in colds (moderate to severe) and can come on quickly after exposure to the viruses that cause the flu (for example, the swine fluvirus strains). In addition, colds don't typically cause death, but the flu is noted to cause death due to respiratory failure in some people.
When should I call the doctor about my cold or the flu?
If a person develops trouble breathing, has a severe sore throat, has a cough that produces green-colored mucus, has chest pain, or develops a high and persistent fever, that person should be seen by their doctor. If you suspect you have the flu and are pregnant, are over 50, have a weakened immune system for any reason, or have ongoing medical problems such as diabetes, you are at higher risk for developing complications due to the flu and should contact your physician. If you have a child under 2 years of age or have a friend or relative living in long-term care facility with flu-like symptoms, their doctors need to be notified.
How do health care professionals diagnose a cold and/or the flu?
Generally, health care professionals distinguish between the cold and the flu by running a rapid influenza diagnostic test, usually done within about 30 minutes. Depending on which test is used, the results can vary but most health care practitioners, including emergency medicine personnel, utilize this test. If the test is negative, patients probably have a cold unless their symptoms and signs become more severe.
What are treatments, medicines, and home remedies for the common cold and the flu?
Prevention of Cold and Flu
Treatment options, medicines, and home remedies for the common cold and flu are almost exactly the same except for a few items that pertain to the more severe disease, the flu.
Common treatments for both diseases include rest and treatment of symptoms as they occur; fever is treated with acetaminophen. Symptoms can be managed with good hydration and over-the-counter cold/flu medications that include suppression of symptoms such as cough, congestion, nausea, and sore throat.
Medicines are usually over-the-counter cold/flu treatments that often are combinations of several drugs like acetaminophen (Tylenol), ibuprofen (Motrin), various cough suppressants, and/or decongestants; for the flu, some health care providers use drugs of the antiviral/neuraminidase inhibitor class (oseltamivir, peramivir, and zanamivir), especially in severe infections.
Home remedies for colds and the flu are similar; vitamin C, zinc, humidified air, steamy showers, gargling with saltwater, compresses to relieve sinus congestion and/or headaches, honey and lemon, ginger, and many other items have been recommended. It is best to check with your physician, especially if you have the flu, before relying on home remedies -- the home remedies mainly reduce symptoms but do not cure the diseases.
Source: Medicine Net